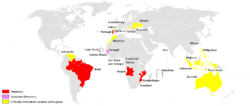
CPLP is a multilateral forum created to deepen mutual friendship and cooperation among its member states.[2]
Through successive enlargements, the Union has grown from the seven founding states—Angola, Brazil, Cape Verde, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Portugal, and São Tomé and Príncipe—to the current nine, with the self-determination of Timor-Leste in 2002[3] and the accession of Equatorial Guinea in 2014[4] at the 10th summit in Dili, Timor-Leste with the issuance of the Dili Declaration.[5] The community is growing from a cultural background to a geopolitical and economical community, as the CPLP is the fourth largest producer of oil in the world and the growing number of larger nations attempting to enter the organization, such as Turkey and Indonesia.[6][7] In 2016, CPLP revised its cooperation protocol in defense, affirming the organization in the promotion of peace and security.[8]
CPLP prime objectives are:[2]
- Political and diplomatic cooperation between its member states, in particular to strengthen its presence in the international arena;
- The cooperation in all areas, including education, health, science and technology, defense, agriculture, public administration, communications, justice, public safety, culture, sports and media;
- The materialization of projects for the promotion and dissemination of the Portuguese language.
In 2005, during a meeting in Luanda, the ministers of culture of the member states declared the 5 May as the Lusophone Culture Day

No comments:
Post a Comment